A longitudinal analysis of the privacy paradox
Tobias Dienlin
1tobias.dienlin@univie.ac.at
Philipp K. Masur
2p.k.masur@vu.nl
Sabine Trepte
3sabine.trepte@uni-hohenheim.de
Abstract
The privacy paradox states that people’s concerns about online privacy are unrelated to their online sharing of personal information. On the basis of a representative sample of the German population, which includes 1403 respondents interviewed at three waves separated by 6 months, we investigate the privacy paradox from a longitudinal perspective. Using a cross-lagged panel model with random intercepts, we differentiate between-person relations from within-person effects. Results revealed that people who were more concerned about their online privacy than others also shared slightly less personal information and had substantially more negative attitudes toward information sharing (between-person level). People who were more concerned than usual also shared slightly less information than usual (within-person level). We found no long-term effects of privacy concerns on information sharing or attitudes 6 months later. The results provide further evidence against the privacy paradox, but more research is needed to better understand potential causal relations.
The privacy paradox states that the information disclosure of Internet users is problematic: Although many people are concerned about their privacy online, they still share plenty of personal information on the web (e.g., Acquisti and Grossklags, 2003). The privacy paradox is of considerable interest to society—it is discussed in newspapers (Frean, 2017), Wikipedia entries (Wikipedia, 2018), designated websites (New York Public Radio, 2018), books (Trepte and Reinecke, 2011), and top-tier academic journals (Acquisti et al., 2015). If the privacy paradox really exists, it should inspire worry: It would suggest that online behavior is irrational and that people are revealing too much of their personal information, which can cause various problems (e.g., Sevignani, 2016). Understanding why people disclose information online and whether or not this is paradoxical therefore represents an important challenge.
However, current research on the privacy paradox has one major limitation. To the best of our knowledge, most empirical studies conducted so far have investigated the privacy paradox from a between-person perspective. By employing empirical tests of relations between people (e.g., cross-sectional questionnaires analyzed with multiple regression or Pearson correlations), studies have analyzed whether people who are more concerned than others also share less personal information than others. Although such a perspective is interesting and represents a viable first step, it cannot make informed claims regarding causality. The privacy paradox, however, implies a causal perspective: Does a person, if they become more concerned about online privacy, then also share less personal information? This mismatch is problematic because although between-person relations are, except for some special cases, a necessary condition for causal within-person effects, they are by no means a sufficient one. For example, it could be that the between-person relation is determined by other third variables. Hence, as the next step in investigating the privacy paradox and to better understand the causal relation between privacy concerns and information sharing, it is necessary to conduct studies with within-person designs.
With this study we aim to answer four major questions. First, on a between-person level, how are concerns about online privacy related to the online sharing of personal information? Second, on a within-person level, is information sharing lower than usual when concerns are higher than usual? Third, what are the potential long-term effects? Are changes in concerns related to changes in information sharing 6 months later and/or vice versa? Fourth, what is the role of privacy attitudes, do they mediate the relation between privacy concerns and information sharing? To best answer and contextualize these questions, we first provide an in-depth theoretical analysis of the privacy paradox, after which we present the empirical results of a longitudinal panel study, which is representative of the German population.
A Brief History of the Privacy Paradox
Acquisti and Grossklags (2003) were among the first to argue that the online disclosure of personal information is paradoxical. “Experiments reveal that very few individuals actually take any action to protect their personal information, even when doing so involves limited costs” (p.1). Three years later, Barnes (2006) discussed the behavior of young people on SNSs, popularizing the term privacy paradox. Barnes considered the following six aspects of online behavior particularly paradoxical: (a) illusion of privacy, (b) high quantity of information sharing, (c) attitude behavior discrepancy, (d) lack of privacy concerns, (e) lack of privacy literacy, and (f) fabrication of false information. Norberg et al. (2007) were one of the first to empirically analyze the privacy paradox explicitly. The study found a mismatch between concerns and behavior, which is aligned with several other experimental studies conducted at the time (Beresford et al., 2012; Hann et al., 2007; Huberman et al., 2005).
While there are various understandings and operationalizations of the privacy paradox (Kokolakis, 2017), subsequent research focused on Barnes’s third tenet, the attitude-behavior discrepancy. Whereas some studies reported that privacy concerns were not significantly related to the disclosure of personal information (e.g., Gross and Acquisti, 2005; Taddicken, 2014; Tufekci, 2008), which lends credence to the privacy paradox, a different set of studies showed significant relations (e.g., Dienlin and Trepte, 2015; Heirman et al., 2013; Walrave et al., 2012), which refutes the privacy paradox.
Notably, in a parallel line of research other studies have also analyzed the relation between privacy concerns and information sharing. However, the term privacy paradox was often not used explicitly. Instead, studies have referred to the so-called privacy calculus, which states that the sharing of personal information online is affected by both the respective costs and the anticipated benefits (Culnan and Armstrong, 1999). By now, several studies have found empirical support for the privacy calculus in various online contexts (e.g., Bol et al., 2018; Dienlin and Metzger, 2016; Krasnova et al., 2010).
Baruh et al. (2017) published the first empirical meta-analysis on the relations between privacy concerns and various forms of social media use (e.g., information sharing or SNS usage). On the basis of 37 studies, Baruh et al. (2017) found a small and significant statistical relation between concerns about online privacy and online information sharing (r = -.13, 95% CI [-.07, -.18]). Another more recent meta analysis by Yu et al. (2020) also finds a significant bivariate relation between privacy concerns and information sharing, albeit smaller (r = -.06, 95% CI [-.01, -.12]). There also exist several systematic literature reviews on the privacy paradox (Barth and Jong, 2017; Gerber et al., 2018; Kokolakis, 2017). Kokolakis (2017) come to the conclusion that “the dichotomy between privacy attitude and behaviour should not be considered a paradox anymore.” (p. 130) However, the authors also note that the privacy paradox is a “complex phenomenon that has not been fully explained yet”. Barth and Jong (2017) are more skeptical, and argue that “attempts to theoretically explain and practically solve the problem of the privacy paradox are still scarce and we feel the subject deserves far more research attention” (p. 1052).
Defining Privacy Concerns and Information Sharing
Privacy is defined as the “[…] voluntary and temporary withdrawal of a person from the general society through physical or psychological means […]” (Westin, 1967: 7). Privacy captures aspects of both volitional control and social separateness (Bräunlich et al., 2020; Marwick and boyd, 2014). People from all cultural backgrounds require privacy to fulfill fundamental needs including personal care, protected communication, intimacy, or sexuality (Altman, 1977; Westin, 1967). Being a universal human right (UN General Assembly, 1948, Art. 12), privacy is essential for safety, psychosocial flourishing, and dignity. It is driven by both individual needs and interpersonal negotiations thereof (Trepte, 2020).
Several dimensions of privacy have been proposed. For example, it is possible to distinguish a vertical and a horizontal level (Masur, 2018). Whereas the vertical level captures privacy from authorities, institutions, or companies, horizontal privacy addresses privacy from peers, colleagues, or other people. When it comes to concerns in general, interestingly they do not seem to be established as a stand-alone theoretical concept in psychology (Colman, 2015). Concerns are usually understood as an uneasy mix of “interest, uncertainty, and apprehension” (Merriam-Webster, 2018). As a theoretical construct, privacy concerns can hence be categorized as an affective motivational disposition. Taken together, concerns about online privacy represent how much an individual is motivated to focus on their control over a voluntary withdrawal from other people or societal institutions on the Internet, accompanied by an uneasy feeling that their privacy might be threatened.
The online sharing of personal information, on the other hand, captures how much person-related information people share when they use the Internet. Information sharing can be differentiated from communication and self-disclosure. Communication is broad, because it comprises all verbal and nonverbal information that is emitted (e.g., Watzlawick et al., 2011). Self-disclosure is more narrow, because it focuses on deliberate revelations about the true self to others, including aspects such as personal fears, values, or plans (e.g., Jourard, 1964). Information sharing is even more specific, because it addresses only person-related information, including information about their age, sex, name, address, health, and finances.
In what follows we hence investigate the two concepts of (a) concerns about online privacy and (b) online information sharing, aiming to investigate how they relate conceptually. In doing so, we adopt and focus on the perspective of individual people.
The Relation Between Privacy Concerns and Information Sharing
Currently, there is a lack of studies that explicitly analyze how behavior is affected by concerns in general. Fortunately, however, we know much about the behavioral effects of related concepts such as attitudes or fears, which all can affect behavior, sometimes profoundly (Fishbein and Ajzen, 2010; Rogers, 1983). Emotions, perhaps the concept most closely related to concerns, have a particularly strong effect on behavior. By causing fight, flight, or freeze reactions, they are a primordial trigger of behavior and are considered to be an adaptive mechanism of evolved species (Dolan, 2002).
Also empirically, concerns have been shown to affect behavior (Hayes and Ross, 1987; Reel et al., 2007). For example, people more concerned about the environment show more environment-related behaviors (Bamberg, 2003). Taken together, it is reasonable to expect that also concerns about online privacy should somehow reflect in the online sharing of personal information.
At the same time, there are some factors that likely diminish the relation. Most prominently, there is the so-called attitude behavior gap (Fishbein and Ajzen, 2010), which states that people sometimes act against their own attitudes. Evidently, not everyone concerned about their physical health exercises regularly. The explanation is simple: Other factors such as subjective norms and perceived behavioral control also determine behavior (Ajzen, 1985), which automatically reduces the impact of attitudes or concerns.
Specifically, two of the most influential factors that affect online information sharing are (a) strong subjective norms (Heirman et al., 2013) and (b) expected benefits (Krasnova et al., 2010). In other words, users often prioritize social support, special offers, or improved services, accepting that their privacy will be diminished. Sometimes, privacy concerns do not relate to information sharing, because users lack the skills, knowledge, or literacy to change their online behavior, creating feelings of apathy or cynicism (Hargittai and Marwick, 2016; Hoffmann et al., 2016). Likewise, personal information is also often shared by others, a phenomenon described as “networked privacy” (Marwick and boyd, 2014), which further reduces the power of individuals to determine how much personal information can be found online. Trepte et al. (2014) listed several factors that can additionally attenuate the relation: lack of strength of concerns, absence of negative personal experiences, or situational constraints due to social desirability. In conclusion, also in the context of the privacy paradox it is not reasonable to expect a perfect relation between attitudes and behaviors. However, we should still expect to find a relation that is small or moderate.
There are also some methodological explanations as to why some studies did not detect statistically significant relations. Researchers are always confronted with the so-called Duhem-Quine problem, according to which it is impossible to test theories in isolation, because empirical tests always rely on auxiliary assumptions (Dienes, 2008). In other words, if a psychological experiment fails, we do not know whether the theory is wrong or the questionnaire subpar. This tenet is particularly relevant for the privacy paradox: Detecting statistical significance for small effects—and, again, we should expect to find small or moderate effects—is more challenging because it means that large samples are necessary to guarantee sufficient statistical power.1 Precisely, in order to be capable of detecting a correlation between privacy concerns and information sharing in 95% of all cases, which Baruh et al. (2017) estimated to be r = -.13, we need a sample of N = 762 people. The reality, however, looks different: In their meta-analysis, Baruh et al. (2017) reported a median sample size of N = 300, which can explain why several studies did not find significant effects.
In conclusion, we expect to find a small significant relation between privacy concerns and information sharing, both on the between-person level (Hypothesis 1) and the within-person level (Hypothesis 2).2
Hypothesis 1: People who are more concerned about their online privacy than others will also be less likely to share personal information online than others.
Hypothesis 2: People who are more concerned about their online privacy than they usually are will also share less personal information online than they usually do.
Long-Term Perspective
Although short-term effects are likely, it is still unclear whether long-term effects exist as well. First, when analyzing potential long-term effects, it is important to choose an interval that is both plausible and relevant. It makes a large difference whether the effects of alcohol consumption on driving performance are tested after say 1 minute, 1 hour, or 1 day. One factor that determines an interval’s optimal length is the stability of the variables (Dormann and Griffin, 2015). Privacy concerns and privacy attitudes are predominantly trait-like constructs with high stabilities, which is why they necessitate longer intervals. Other studies with comparable research questions have therefore used an interval of 6 months (e.g., Valkenburg and Peter, 2009), which we adopt also in this study.
In general, we believe that it should be possible to find long-term effects. It has been argued that privacy concerns affect privacy behavior in the long run (e.g., Heirman et al., 2013). The underlying theoretical mechanism could be that the emotional part of privacy concerns causes (a) motivated information selection and (b) motivated information processing, which is likely to change actual behavior (Nabi, 1999). Specifically, when privacy concerns are higher than usual (e.g., because of experienced or witnessed privacy infringements), people might begin reading more media articles on privacy issues and might also consume these articles more carefully, which could prompt information sharing practices that are more cautious. Also empirically, a study with 290 participants found small negative longitudinal (between-person) relations between privacy concerns and self-disclosure (Koohikamali et al., 2019).
At the same time, the adverse effect seems plausible as well, with two potential outcomes. On the one hand, the long-term relation could be positive: If people start to share more information online, they might become increasingly aware that their privacy is at risk, thereby stirring concern (Tsay-Vogel et al., 2018). On the other hand, the long-term relation might also be negative: When people share more personal information online they might become accustomed to doing so, which potentially reduces concern [for example, due to the mere exposure effect; Zajonc (1968)]. Finally, there could also be no long-term relation at all: People might have already become used to sharing information online, which stifles further cognitive or emotional processing. This rationale is central to privacy cynicism (e.g., Hoffmann et al., 2016).
Research Question 1.1: Do changes in concerns about online privacy affect the online sharing of personal information 6 months later?
Research Question 1.2: Do changes in the online sharing of personal information affect concerns about online privacy 6 months later?
The Role of Attitudes
It has been argued that privacy attitudes could bridge the gap between concerns and information sharing (e.g., Dienlin and Trepte, 2015). In contrast to general and implicit privacy concerns, privacy attitudes capture a more explicit, specific cognitive appraisal (Tsay-Vogel et al., 2018). Because general dispositions oftentimes affect more specific appraisals (Fishbein and Ajzen, 2010), general concerns about privacy may similarly affect more specific privacy attitudes (Dienlin and Trepte, 2015). This reasoning follows the rational choice paradigm (Simon, 1955), which maintains that behavior is always at least partially influenced by specific convictions, attitudes, and cost-benefit analyses. Therefore, although both variables are related to information disclosure, attitudes are likely the better predictor. Also empirically, a study of 1,042 youths from Belgium found that the relation between privacy attitudes and disclosure intentions of personal information was strong (r = .56), whereas the relation between privacy concerns and disclosure intentions was only moderate [r = -.29; Heirman et al. (2013)].
Hypothesis 3.1: People who are more concerned about their online privacy than others will also hold a less positive attitude toward the online sharing of personal information than others.
Hypothesis 3.2: People with a more positive attitude toward the online sharing of personal information than others will also share more information online than others.
Hypothesis 4.1: People who are more concerned about their online privacy than they usually are will also hold a less positive attitude toward the online sharing of personal information than they usually do.
Hypothesis 4.2: People with a more positive attitude toward the online sharing of personal information than they usually have will also share more information online than they usually do.
Concerning the potential long-term relations of privacy attitudes, we are confronted with the same situation mentioned above. Because we are not aware of research on long-term relations, several scenarios seem plausible. Attitudes could either have long-term relations or not, and information sharing could either foster privacy attitudes or diminish them.
Research Question 2.1: Do changes in concerns about online privacy affect attitudes toward the online sharing of personal information 6 months later?
Research Question 2.2: Do changes in attitudes toward the online sharing of personal information affect concerns about online privacy 6 months later?
Research Question 3.1: Do changes in attitudes toward the online sharing of personal information affect the online sharing of personal information 6 months later?
Research Question 3.2: Do changes in the online sharing of personal information affect attitudes toward the online sharing of personal information 6 months later?
Method
Procedure and Respondents
This study is part of a large-scale project which investigates the development of privacy and self-disclosure, including several other variables. Other publications linked to the project can be accessed at https://osf.io/y35as/. The data come from a longitudinal paper-and-pencil questionnaire study, in which a representative sample of the German population (16 years and older) was surveyed on overall five occasions. The data can be downloaded from https://doi.org/10.7802/1937.
The first three waves were collected from May 2014 to May 2015, with intervals of 6 months each. The last two waves were collected on May 2016 and May 2017, and had an interval of one year. Because we hypothesized the effects to take place across half a year, the last two waves were not included in the analyses presented here. First, a sample of 14,714 potential respondents was drawn from a representative omnibus survey in Germany (ADM master sample), using a random last-two-digit dialing procedure. In this CATI screening, 5,286 respondents agreed to participate in all following waves. Wave 1 was completed by 3,278 respondents (response rate: 38%), Wave 2 by 2,448 respondents (attrition rate: 25%), and Wave 3 by 2,021 respondents (attrition rate: 17%). We filtered respondents who never used the Internet at all waves, answered fewer than 50% of the items in each scale for at least one wave, provided inconsistent birth-dates across measurements, or did not report sociodemographic variables. The final sample consisted of n = 1,403 respondents.
In the final sample, the rate of missing data was 5.4%. Visual inspection of the missing value patterns as well as the non-parametric test by Jamshidian et al. (2014) suggested that all missing values could be considered missing at random (p = .514). Therefore, Full Information Maximum Likelihood estimation was conducted using all available data. The average age was 54 years (SD = 15 years), and 49% were male. About 39% reported that they had graduated from college.
Measures
We tested the factorial validity of all measures using confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). Each CFA included the items from all three waves. For each item, factor loadings were constrained to be equal across waves. Constrained and unconstrained models were compared using \(\chi^2\) differences tests. All results were nonsignificant, suggesting longitudinal factorial invariance. The measures showed good composite reliability in all three waves. Graphical displays of the variables’ distributions showed that privacy concerns were skewed to the left, privacy attitudes were normally distributed, and information sharing was skewed to the right (Figure @ref(fig:Distributions), diagonal). We calculated intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) to quantify how much variance in the variables’ factor scores could be attributed to between-person differences. An English translation of the original German items can be found in the online supplementary material.
Concerns about online privacy
Privacy concerns were measured as a second-order factor. Three self-developed items captured the vertical dimension (e.g., “How concerned are you that institutions or intelligence services collect and analyze data that you disclosed on the Internet?”), and three items by Buchanan et al. (2007) captured the horizontal dimension (e.g., “How concerned are you that people that you do not know might obtain information about you because of you online activities?”). Respondents rated all items on a 5-point scale ranging from 1 (not at all concerned) to 5 (very concerned). The means were Mt1 = 3.67, Mt2 = 3.62, Mt3 = 3.59, and the standard deviations SDt1 = 0.88, SDt2 = 0.89, and SDt3 = 0.90. The two-dimensional model fit the data well, \(\chi^2\)(118) = 661.17, < .001, cfi = .97, rmsea = .06, 90% CI [.05, .06], srmr = .04. The reliability was high (\(\omega\)t1 = .95, \(\omega\)t2 = .96, \(\omega\)t3 = .97). Overall, 73.8534006% of the measure’s variance was explained by differences between persons.
The online sharing of personal information
To measure respondent’s level of information disclosure, they were asked how often they disclosed 10 different pieces of information on the Internet (European Commission, 2011). The exact question was: “How often do you disclose the following pieces of information online (i.e., on the Internet)?” Each item was answered on a 5-point scale ranging from 1 (never) to 5 (daily). Factor analyses suggested a second-order factor structure with five first-order factors of two items each. The first first-order factor subsumed financial and medical information, the second first and last name, the third place of residence and street (including house number), the fourth email address and phone number, and the fifth information about education and current job. The means were Mt1 = 2.12, Mt2 = 2.13, Mt3 = 2.10, and the standard deviations SDt1 = 0.66, SDt2 = 0.64, and SDt3 = 0.61. The model fit the data adequately, \(\chi^2\)(375) = 2527.69, < .001, cfi = .95, rmsea = .06, 90% CI [.06, .07], srmr = .06. The reliability was high (\(\omega\)t1 = .91, \(\omega\)t2 = .92, \(\omega\)t3 = .91). Overall, 64.2916969% of the measure’s variance was explained by differences between persons.
Attitudes toward the online sharing of personal information
Respondents’ attitudes toward disclosing personal information online were captured with 10 items that measured the general appraisal of disclosing the same 10 pieces of information (European Commission, 2011). Adhering to the principle of compatibility (Fishbein and Ajzen, 2010), the items were parallel to those of the actual disclosure scale. Specifically, we asked: “Do you think that it is sensible to disclose the following pieces of information online (i.e., on the Internet)?” The scale ranged from 1 (not at all sensible) to 5 (very sensible). The means were Mt1 = 3.67, Mt2 = 3.62, Mt3 = 3.59, and the standard deviations SDt1 = 0.88, SDt2 = 0.89, and SDt3 = 0.90. The second-order model with five first-order factors showed an adequate model fit, \(\chi^2\)(375) = 2683.43, < .001, cfi = .93, rmsea = .07, 90% CI [.06, .07], srmr = .08. The reliability was high (\(\omega\)t1 = .88, \(\omega\)t2 = .89, \(\omega\)t3 = .87). Overall, 59.1868702% of the measure’s variance was explained by differences between persons.
Data Analysis
We follow the recommendation by Lakens, Adolfi, et al. (2018) and first justify the choice of our alpha level. We determined adequate error margins by considering the potential implications of both false positive and false negative findings (i.e., alpha and beta errors): On the one hand, if we committed an alpha error, we would wrongfully conclude that people’s concerns and behaviors are consistent. Communicating such a false result to the public might unjustly reassure people when they should be more alert. On the other hand, if we committed a beta error, we would wrongfully conclude that individuals behave paradoxically. Communicating such a false result would unjustly accuse people of implausible behavior, potentially causing unnecessary distress or reactance. We consider both errors to be equally detrimental. Hence, we chose balanced error rates, setting a maximum error rate of 5% for both alpha and beta. As the smallest effect size of interest [SESOI; Lakens, Scheel, et al. (2018)], we chose to consider effects that are at least small [i.e., standardized coefficients above \(\beta\) = .10; Cohen (1992)] as able to offer empirical support for our theoretical hypotheses. Significantly smaller effects were not considered able to offer support. The six hypotheses were tested with a one-tailed approach and the six research questions with a two-tailed approach. On the basis of the balanced alpha-beta approach with a maximum error probability of 5%, a desired power of 95%, and an SESOI of \(\beta\) = .10, we calculated a minimum sample size of 1,293 respondents. Given the final sample size of 1,403 respondents, alpha and beta errors were balanced for our hypotheses (research questions) when we used a critical alpha of 3% (4.2%), resulting in a power of 97% (95.8%) to detect small effects.
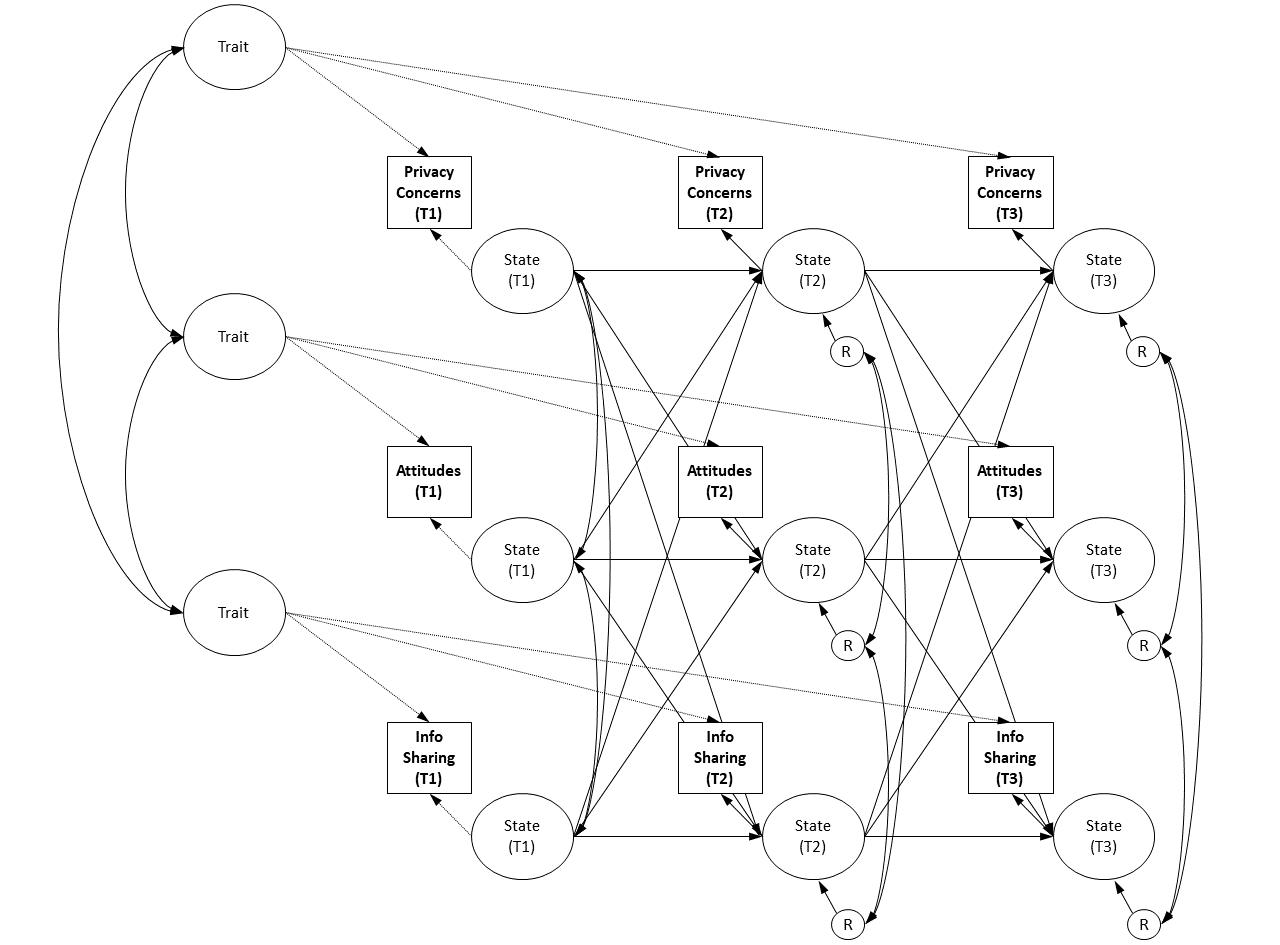
The estimated random-intercept cross-lagged panel model (RI-CLPM).
The data were analyzed using of a random-intercept cross-lagged panel model (RI-CLPM, Hamaker et al., 2015). For a visualization, see Figure @ref(fig:RICLPM). Note that in contrast to regular cross-lagged panel models (CLPMs), RI-CLPMs can separate between-person variance from within-person variance. We used factor scores as observed variables to represent the variables’ latent structure more closely. We tested H1, H3.1, and H3.2 by correlating the random intercepts, which represent the respondents’ individual mean scores across all three waves. We tested H2, H4.1, and H4.2 by correlating the respondents’ within-person variance at T1, which captures their specific deviation at T1 from their overall score. We tested all research questions by regressing variables on all other measures obtained 6 months earlier. Given that we had three points of measurement, this resulted in two estimates for each research question. As we did not assume longitudinal effects to differ across time, they were constrained to be equal across all waves, which produces one single general measure of each effect instead of two time-specific ones. (We later tested this assumption empirically. As expected, the model with constrained effects did not show significantly reduced model fit, \(\chi\)2(9) = .114, p = 14.25, which supports that effects did not change over time.) Fit was assessed according to the common criteria as described by Kline (2016). The final model fit the data well, \(\chi^2\)(15) = 25.18, = .048, cfi = 1.00, rmsea = .02, 90% CI [< .01, .04], srmr = .01.
For the analyses, we used R (Version 4.3.1; R Core Team, 2018) and the R-packages GGally (Version 2.1.2; Schloerke et al., 2018), ggplot2 (Version 3.4.4; Wickham, 2016), lavaan (Version 0.6.15; Rosseel, 2012), MissMech (Jamshidian et al., 2014), MVN (Version 5.9; Korkmaz et al., 2014), psych (Version 2.3.3; Revelle, 2018), pwr (Version 1.3.0; Champely, 2018), semTools (Version 0.5.6; Jorgensen et al., 2018), and sjstats (Version 0.18.2; Lüdecke, 2019). The code, additional analyses (e.g., ICCs or analyses of invariance), and a reproducible version of this manuscript can be found on the manuscript’s companion website at https://tdienlin.github.io/privacy-paradox-longitudinal/.
Results
In a first descriptive step, we analyzed the variables’ bivariate relations. All variables associated with the hypotheses showed correlations that were in line with our theoretical rationales (Figure @ref(fig:Distributions), above the diagonal).
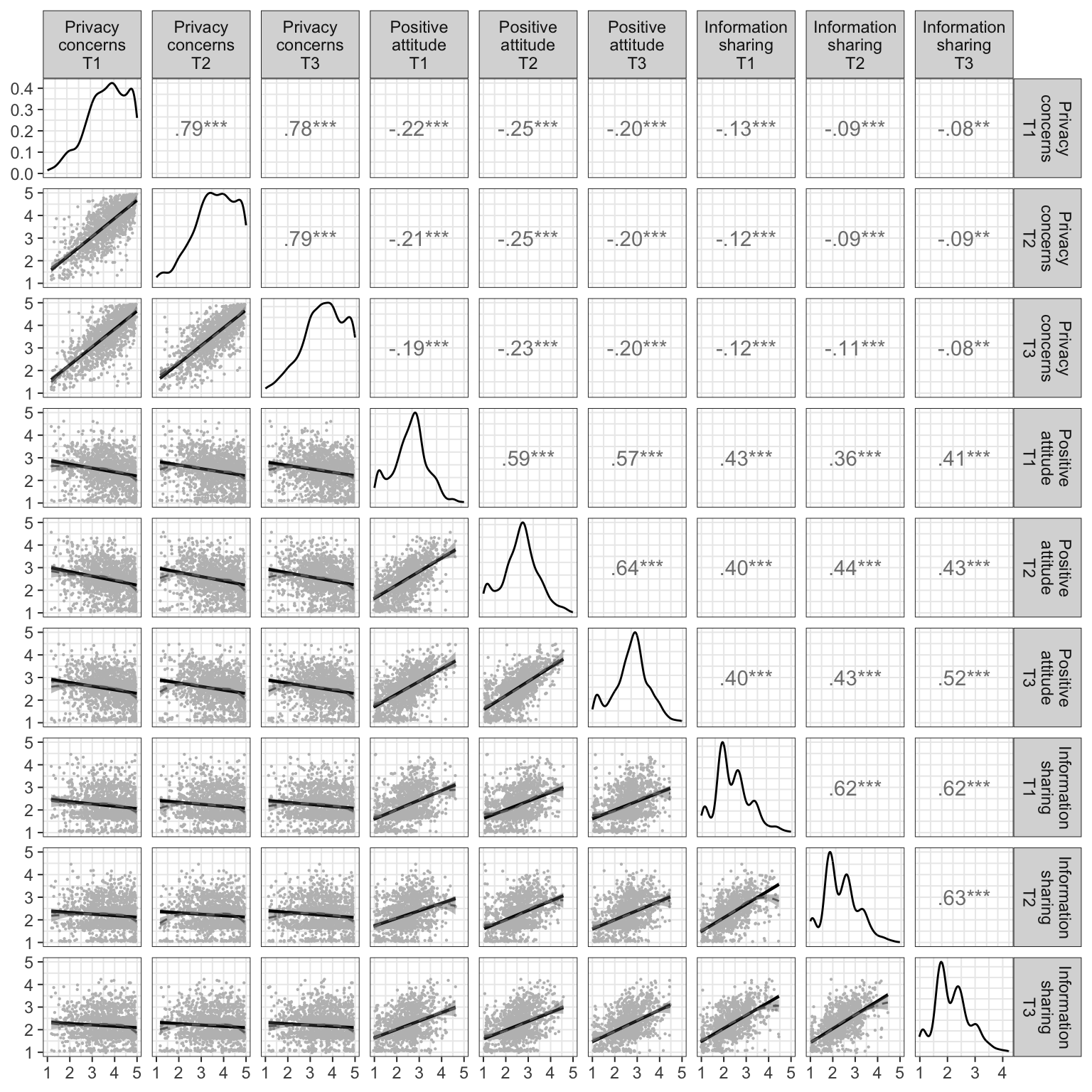
Results of the bivariate relations. Above the diagonal: zero-order correlation matrix; diagonal: density plots for each variable; below the diagonal: bivariate scatter plots for zero-order correlations. Solid regression lines represent linear regressions, dashed regression lines represent quadratic regressions. Calculated with the variables’ latent factor scores.
Hypothesis 1 predicted that people reporting higher concerns about online privacy than others would also be less likely to share personal information online than others. Results revealed that the random intercepts of the two variables were significantly correlated (\(\beta\) = -.09, = -0.03, 95% CI [-0.05, -0.01], = -2.57, = .005). Hence, respondents who—on average across all three waves—were more concerned about their privacy than others also shared slightly less personal information online. The effect was small. When looking at the standardized effect’s confidence interval (i.e., \(\beta\) = -.09, 95% CI [-.15, -.02]), it was not significantly smaller than our SESOI of \(beta\) = .10. Thus, Hypothesis 1 was supported.
Hypothesis 2 proposed that if people perceived more concerns about their online privacy than they usually do, they would also share less personal information online than they usually do. Results revealed a small significant correlation (\(\beta\) = -.10, = -0.02, 95% CI [-0.03, > -0.01], = -2.37, = .009), suggesting that if respondents were more concerned about their online privacy at T1 than usual, they also shared less personal information online at T1 than usual. In conclusion, the results supported Hypothesis 2.
With Research Question 1.1, we analyzed the longitudinal relation of concerns about online privacy and the online sharing of personal information 6 months later. No significant lagged effect across 6 months was found (\(\beta\) = .01, = 0.01, 95% CI [-0.05, 0.07], = 0.41, = .683). With Research Question 1.2, we investigated the longitudinal relation of the online sharing of personal information and concerns about online privacy 6 months later, again revealing no significant effect (\(\beta\) = -.03, = -0.03, 95% CI [-0.09, 0.04], = -0.80, = .422).
Hypothesis 3.1 predicted that people who perceived more privacy concerns than others would also hold more negative attitudes toward the online sharing of personal information than others. The results revealed a medium-sized negative correlation between the two variables on the between-person level (\(\beta\) = -.31, = -0.11, 95% CI [-0.14, -0.08], = -8.46, < .001). Thus, people who—on average across all three waves—reported being more concerned about their online privacy relative to the rest of the sample, were also substantially more likely to hold a more negative attitude toward the online sharing of personal information. The results therefore supported Hypothesis 3.1. Hypothesis 3.2 stated that people who held more positive attitudes toward the online sharing of personal information than others would also share more personal information online than others. Results showed a very strong between-person correlation between the two variables (\(\beta\) = .66, = 0.15, 95% CI [0.13, 0.17], = 15.12, < .001). In other words, when averaged across all three waves, if people had more positive attitudes toward the online sharing of personal information than others, they were much more likely to actually share personal information online. In conclusion, the results supported Hypothesis 3.2.
Hypothesis 4.1 proposed that people who perceived more privacy concerns than usual would also hold more negative attitudes toward the online sharing of personal information than usual. The results did not reveal a significant effect (\(\beta\) = -.06, = -0.01, 95% CI [-0.03, < 0.01], = -1.38, = .084). Hypothesis 4.2 proposed that people who held more positive attitudes toward the online sharing of personal information than usual would also share more personal information online than usual. Results showed a moderate within-person correlation between the two variables (\(\beta\) = .15, = 0.03, 95% CI [0.02, 0.05], = 4.01, < .001), which indicates that when respondents had more positive attitudes at T1 than usual, they also shared more personal information than usual. In conclusion, the results supported Hypothesis 4.2.
With Research Question 2.1, we analyzed the longitudinal relations of concerns about online privacy and positive attitudes toward the online sharing of personal information. No significant effect was found (\(\beta\) = -.02, = -0.02, 95% CI [-0.09, 0.06], = -0.47, = .641). Regarding Research Question 2.2, again no significant longitudinal relations emerged between privacy attitudes and privacy concerns 6 months later (\(\beta\) < .01, < 0.01, 95% CI [-0.06, 0.06], = 0.06, = .951).
Research Question 3.1 asked whether changes in attitudes toward the online sharing of personal information would affect changes in personal information sharing 6 months later. No significant effect was found (\(\beta\) > -.01, > -0.01, 95% CI [-0.06, 0.05], = -0.07, = .947). Next, Research Question 3.2 asked whether changes in the online sharing of personal information would affect attitudes toward the online sharing of personal information 6 months later. Again, no significant effect was found (\(\beta\) = .04, = 0.04, 95% CI [-0.03, 0.11], = 1.15, = .249).
Table @ref(tab:Results1) presents an overview of all results.
| Effect | b | ll | ul | beta | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between-person correlations across all waves | |||||
| Privacy concern <-> information sharing | -0.03 | -0.05 | -0.01 | -.09 | .005 |
| Privacy concern <-> positive attitude | -0.11 | -0.14 | -0.08 | -.31 | < .001 |
| Positive attitude <-> information sharing | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.17 | .66 | < .001 |
| Within-person correlations at T1 | |||||
| Privacy concern <-> information sharing | -0.02 | -0.03 | > -0.01 | -.10 | .009 |
| Privacy concern <-> positive attitude | -0.01 | -0.03 | < 0.01 | -.06 | .084 |
| Positive attitude <-> information sharing | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.05 | .15 | < .001 |
| Within-person effects across 6 months | |||||
| Privacy concern -> information sharing | 0.01 | -0.05 | 0.07 | .01 | .683 |
| Information sharing -> privacy concern | -0.03 | -0.09 | 0.04 | -.03 | .422 |
| Privacy concern -> positive attitude | -0.02 | -0.09 | 0.06 | -.02 | .641 |
| Positive attitude -> privacy concern | < 0.01 | -0.06 | 0.06 | < .01 | .951 |
| Positive attitude -> information sharing | > -0.01 | -0.06 | 0.05 | > -.01 | .947 |
| Information sharing -> positive attitude | 0.04 | -0.03 | 0.11 | .04 | .249 |
Note. The between-person correlations represent interpersonal relations. For example, results showed that people who were more concerned than others, averaged across all three waves, also shared less information than others. The within-person parameters reflect how intrapersonal changes in one variable are related to intra-personal changes in another. For example, results showed that if a person was more concerned at T1 than usual, they also shared less information than usual.
In an additional analysis, we also tested the same model with a 1 year interval, which allowed to include data spanning until winter 2016 and 2017. Most effects remained the same. For example, we again found that people more concerned than others were less positive regarding information sharing (r = -.36, p < .001 ) and shared less information (r = -.15, p = .002). Likewise, people more positive toward data sharing than others also shared substantially more data (r = .66, p < .001). Because including these two additional waves significantly reduces sample size, and because we consider it more likely that effects take place more immediately, these results should be considered exploratory. For an overview of the results, see the additional analyses on our companion website (Section 2.1.2.7).
Discussion
Most research on the privacy paradox suggests a significant small effect of privacy concerns on the online sharing of personal information (e.g., Baruh et al., 2017). However, whereas the theoretical premise of the privacy paradox addresses a within-person effect, most empirical studies have analyzed only between-person relations. On the basis of a representative sample of the German population, from which three waves of data separated by 6 months were collected, we hence analyzed the privacy paradox by differentiating general between-person relations, short-term within-person relations, as well as long-term within-person effects. Together, this approach allows for informed inferences about the variables’ causal relationship.
The results of the between-person analyses showed that people who were more concerned about their privacy than others were slightly less likely to share personal information. In addition, people who were more concerned about their privacy than others also held substantially more negative attitudes toward disclosing personal information online. Notably, we found a very strong between-person correlation between attitudes toward information sharing and actual information sharing, which shows that typical online disclosure can be predicted precisely by a person’s attitude. Taken together, the cross-sectional results are in line with the extant literature: The between-person correlation of privacy concerns and information sharing found in this study (i.e., \(\beta\) = -.09) fall within the 95% confidence interval of the effect reported by Baruh et al. (2017) (i.e., r = -.13, 95% CI [-.07, -.18]). Notably, the between-person correlations reported here represent averaged measurements across three waves, which makes the findings more robust than typical one-shot measures.
In conclusion, this study suggests that the privacy paradox does not exist on a between-person level. The differences between people with regard to their online information sharing behavior can be explained by differences in their privacy concerns to a small extent, and by differences in their privacy attitudes to a large extent. The more specific we become, the better we can explain online behavior: Whereas privacy concerns are related only weakly to online information sharing (e.g., Baruh et al., 2017), more specific risks perceptions are related to behavior more closely (e.g., Bol et al., 2018; Yu et al., 2020), whereas behavioral attitudes are the best predictors (Dienlin and Trepte, 2015).
The within-person results showed that when a person’s privacy concerns are higher than usual, the same person also shared slightly less information online than usual. Moreover, people who developed more positive attitudes toward the online sharing of personal information than usual, also shared substantially more personal information online. Together, changes in concerns and attitudes are therefore related to changes in behavior, which speaks against the privacy paradox also on the within-person level.
We did not find any long-term effects, however. Changes in both privacy concerns and attitudes toward the online sharing of personal information were not related to any meaningful changes in the online sharing of personal information 6 months later (and vice versa). As an explanation, it might be the case that changes in privacy concern affect information sharing more immediately. To test this assumption, we would need studies with shorter intervals (Keijsers, 2016). Moreover, given that the directions of most longitudinal relations were in line with the between-person and within-person relations, longitudinal effects might indeed take place, but only that they are very small. Of course, it could also be that longterm longitudinal effects do not exist.
Limitations
The data were collected between May 2014 and May 2015—hence, after the Snowden revelations in 2013, but before the Equifax data breach in 2017, the Cambridge Analytica data breach in 2018, or the implementation of the General Data Protection Regulation in 2018. Such sweeping events, however, could affect privacy concerns, online behavior, or their mutual relation, which would limit the generalizability of our results. Although this is an important caveat, we have reason to believe that our findings are largely robust. First, additional analyses showed that the within-person relationships were stable across waves (a period of 1 year). Second, another set of additional analyses showed that most effects remained stable until winter 2017. Third, records of online search terms revealed that although interest in privacy-related topics and privacy-enhancing technologies increased after the Snowden revelations, it returned to prior levels after only two weeks (Preibusch, 2015). It thus seems that levels of privacy concerns and information sharing, as well as their mutual relationship, are largely robust.
In asking how much information respondents share when using the Internet in general, we automatically aggregated different platforms, contexts, and situations. However, privacy mechanisms can differ largely across contexts (Nissenbaum, 2010) and situations (Masur, 2018). Our broad perspective, therefore, is somewhat problematic and limits our capacity to understand and predict the behavior of individual people in specific situations. At the same time, aiming to maximize generalizability, we were able to extract some general underlying patterns, which can serve as a starting point for more contextualized analyses (see below).
Some of the effect sizes reported in this study are potentially not large enough to refute the privacy paradox completely. On the one hand, they could be a manifestation of the so-called “crud factor” (Meehl, 1990: 204), which states that all psychosocial measures are related to one another to some extent. On the other hand, additional factors such as expected benefits might play a more important role (Dienlin and Metzger, 2016). In conclusion, although our results suggest that privacy concerns and privacy attitudes are correlated with information sharing, the importance of privacy concerns should not be exaggerated. The effects could be larger, and other variables play a role as well.
In this study we measured information sharing using self-reports. However, self-reports of frequent and routine behaviors are often imprecise and unreliable (Scharkow, 2016). This represents a profound limitation of our study; whenever possible, future studies should aim to collect objective observations of specific types of behavior.
Finally, please note that the hypotheses presented in this study were not formally preregistered. At the time when the study was conceived in 2014, we were not yet aware of the importance of preregistration.
Future Research
We emphasize that when analyzing the privacy paradox we are likely dealing with small effects (Baruh et al., 2017). Hence, to detect these small effects reliably we need large samples. This is often not the case (Baruh et al., 2017). In conclusion, it is crucial to use statistical designs that allow for sufficient statistical power.
Next, evidence of within-person longitudinal effects is still missing. Although we found significant within-person correlations at T1, they were absent across the 6-month intervals. Together, this suggests that longitudinal effects might exist, but that they take place on a different time interval. Future research could hence probe different intervals. For theoretical reasons (e.g., due to availability heuristics), it is plausible to use short intervals; for statistical reasons (e.g., because of the high stability of privacy concerns), it would also make sense to test longer intervals (Dormann and Griffin, 2015).
In general, we emphasize that our findings should not be overgeneralized. They are conditional on the data we collected, the methods we applied, and the theoretical perspectives we adopted. We stress that analyzing the privacy paradox in other contexts using alternative approaches will likely lead to different results. Although we argue that in most circumstances privacy concerns and behavior should correlate modestly, the exact extent depends on a many boundary conditions. Future research should hence explicitly analyze different contexts (Nissenbaum, 2010) and situations (Masur, 2018). Building on Kokolakis (2017), we suggest to analyze the following boundary conditions:
- context (e.g., professional, social, commercial, or health-related);
- situation (e.g., new, habitualized, or unexpected);
- mood (e.g., positive vs. negative);
- extent of control (high vs. low);
- type of information processing applied (implicit, heuristic, or peripheral vs. explicit, analytic, or central);
- existence of bias (e.g., overconfidence, optimism, comparative optimism, or hyperbolic discounting);
- type of information (e.g., sensitive vs. superficial, biographic, or person-related);
- benefit immediacy and risk diffusion (high vs. low);
- object of investigation (e.g., individual people, interactions between people, developmental perspectives, critical incidents, societal structures, or historical developments).
Specifically, we encourage analyzing privacy behaviors also from a situational perspective, accounting for temporal needs, interpersonal perceptions, contextual cues, or characteristics of communication channels (Masur, 2018). For example, whereas general levels of information sharing are likely best explained using privacy concerns, situational information sharing might be best explained using privacy heuristics (Sundar et al., 2013).
Next to these theory-related boundary conditions there are also methodological ones:
- analysis design and perspective (e.g., theoretical, experimental, questionnaire-based, interview-based, ethnographic, or computational);
- quality of measurement (high vs. low; low quality less likely to detect statistical significance);
- sample size (small vs. large; small samples less likely to detect statistical significance);
- statistical analysis (e.g., SEM vs. Regression; analyses without error control less likely to find statistical significance);
- operationalization (e.g., concerns vs. risk perceptions vs. behavioral attitudes; the more specific, the stronger the relation).
Conclusion
Being able to show that online behaviors are not paradoxical can be socially relevant. Consider the similar case of fear appeals and protective behavior, where there is also only a small correlation (Witte and Allen, 2000). However, fear appeals are used in public campaigns nonetheless, oftentimes to much success (Wakefield et al., 2010). Likewise, proclaiming that the online sharing of personal information is not paradoxical and that concerns about online privacy matter, could lead to more cautious and reflective behavior. It is probably no coincidence that the General Data Protection Regulation, which strengthens the privacy rights of consumers, was passed in Europe, where privacy concerns are particularly pronounced (European Commission, 2015).
In sum, this study showed that when people were more concerned about their privacy, they also shared a little less personal information about themselves online. If respondents considered sharing personal information to be insensible, they disclosed substantially less information. Together, these findings do not support the existence of a privacy paradox, at least in this particular context and operationalization. No evidence of long-term effects was found, however. Further research is needed to understand the potential causal interplay of concerns, attitudes, and behavior.
References
Statistical power describes the probability of statistically detecting an effect that exists empirically. Only with high statistical power is it possible to make valid claims about an effect’s existence (Cohen, 1992).↩︎
To explain, with Hypothesis 1, we compare different people with one another by analyzing their average values across all measurements. In other words, does a person, who is generally more concerned than others, also generally share less information than others? With Hypothesis 2, we compare specific measurements within the same person. In other words, does a person, if they are more concerned on T1 than on average, share more or less information on T1 than on average?↩︎